This page provides an introduction to Google Ads, tips for successful Google Ads operation, various options and suggestions, and how to receive Ad Grants as an NPO.Introduction to Google Ads
Google, as a dominant global search engine, provides a wide range of advertisement choices to companies. Google Ads allows you to reach anyone who uses Google to search for information, products and services online. If properly used, it has the potential to earn you a large number of people whom your product/service is targeting. Eventually, Google Ads is most likely to lead to increased traffic and customers to your shop/webpage.
Reasons why Google Ads can be the optimal marketing platform
Here are the reasons why you would want to use Google Ads for your marketing:
- Massive user base
Google is the dominant search engine globally. Google owns a massive user base widespread around the world. It is the biggest marketing platform in most cases.
- Capabilities that allow a wide range of targeting
Google’s capability in the management of information systems is well-known. Its massive number of users can be categorised into a wide range of demographic/geographic characteristics which in turn allows you to accurately set your target audience as well as gain insights from their behavioural data.
- Full control and flexibility in your marketing
Google Ads gives you full control of your campaigns/advertisements. You can set your monthly budgets for your advertisement and Google automatically optimise the exposure of your advertisement in accordance with your proposed budget. On top of the budget flexibility, you are also offered a wide range of types of advertisement you can choose from, further optimising your advertisement/campaign in accordance with your target audience and budget.
- Harness intention
Google users are looking for you, in other words, their underlying intention of ‘search’ is to find information/products/services. For example, customers wouldn’t like to see advertisements on their social media because they are unlikely to be looking for them.
- Low complexity
Google Ads has so many different options for you to choose from and automatically optimise your advertisement distribution. This entails far less complexity compared to Search Engine Optimisation (SEO).
Recommended Videos for Beginners
Type of Advertisements Available
Google Ads offers a wide range of advertisement types for your products/services/campaigns.
You must understand what they are in order to make optimal decisions regarding your online advertisement, but it won’t be difficult to understand, I am confident that all of these Google ads are what you’ve been seeing regularly unless you’ve lived under a rock in last two decades.
1. Search Ads: Text ads on Google’s search results
Text-based ads on search results allow you to reach people when they are searching on Google for the products or services you offer.
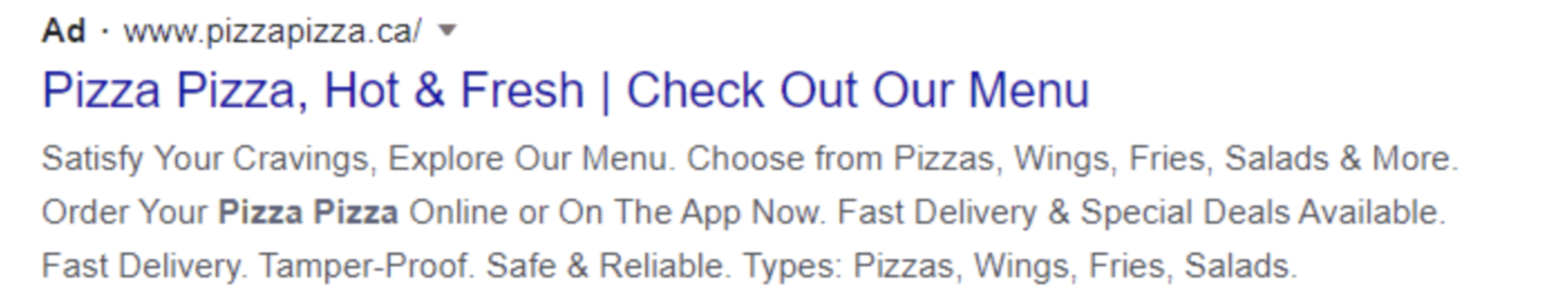
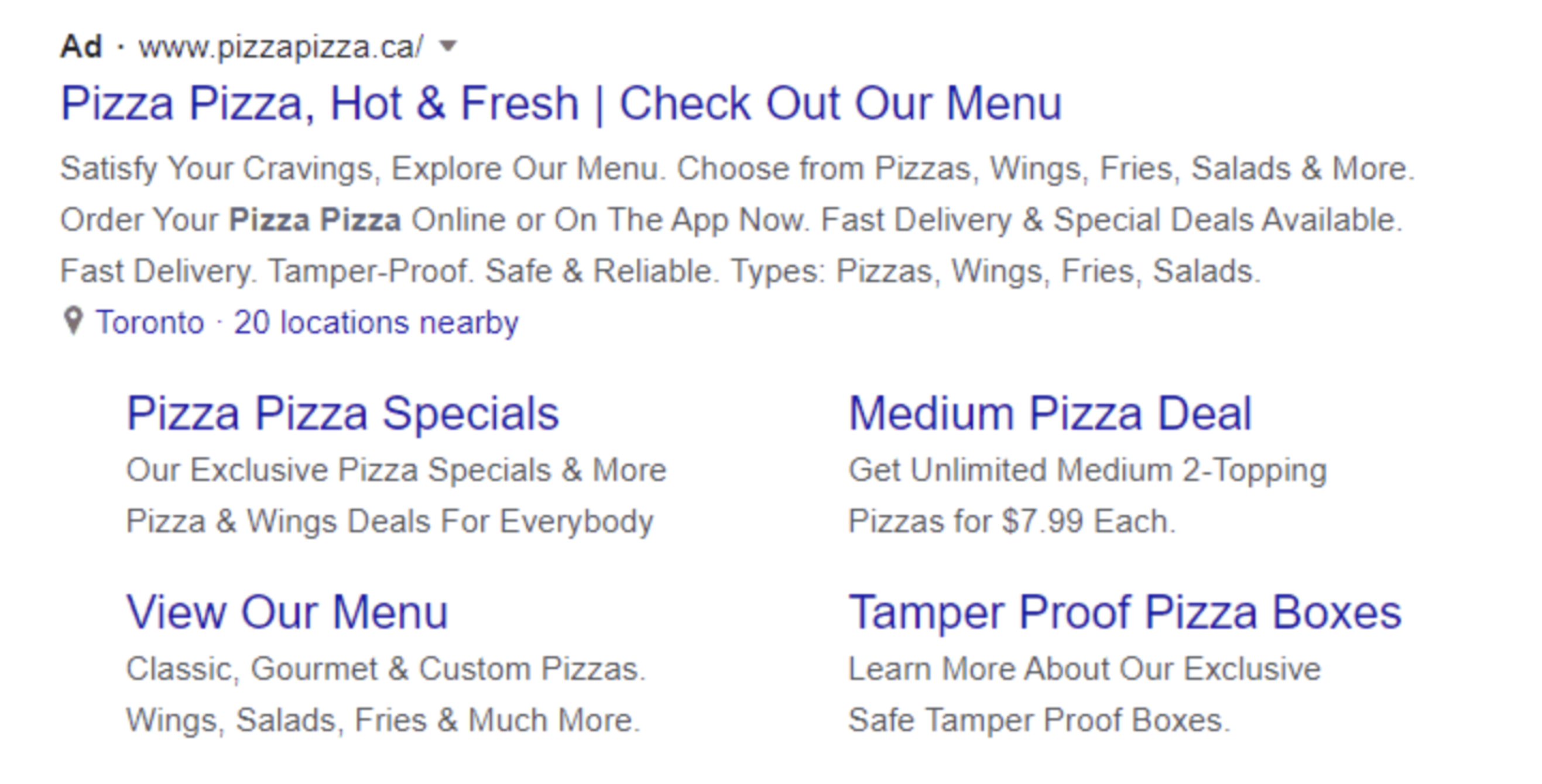
Key benefits:
- Easy setup
- Typically include a headline, URL, and descriptive text
- Show up on the search and display networks
- Highly specific targeting
If you want to display further information such as location, call, subheadings and site links, you can use ‘ad extensions’ as shown above on the right.
2. Display Ads
Display Ads has ‘responsive’ features and it is specifically for displaying the ads and banners in Google’s extremely wide display network.
In responsive display ads, Google allows you to enter multiple versions of headlines and ad copy for Google to select the best performing ads to display to users after a certain amount of data experiment.
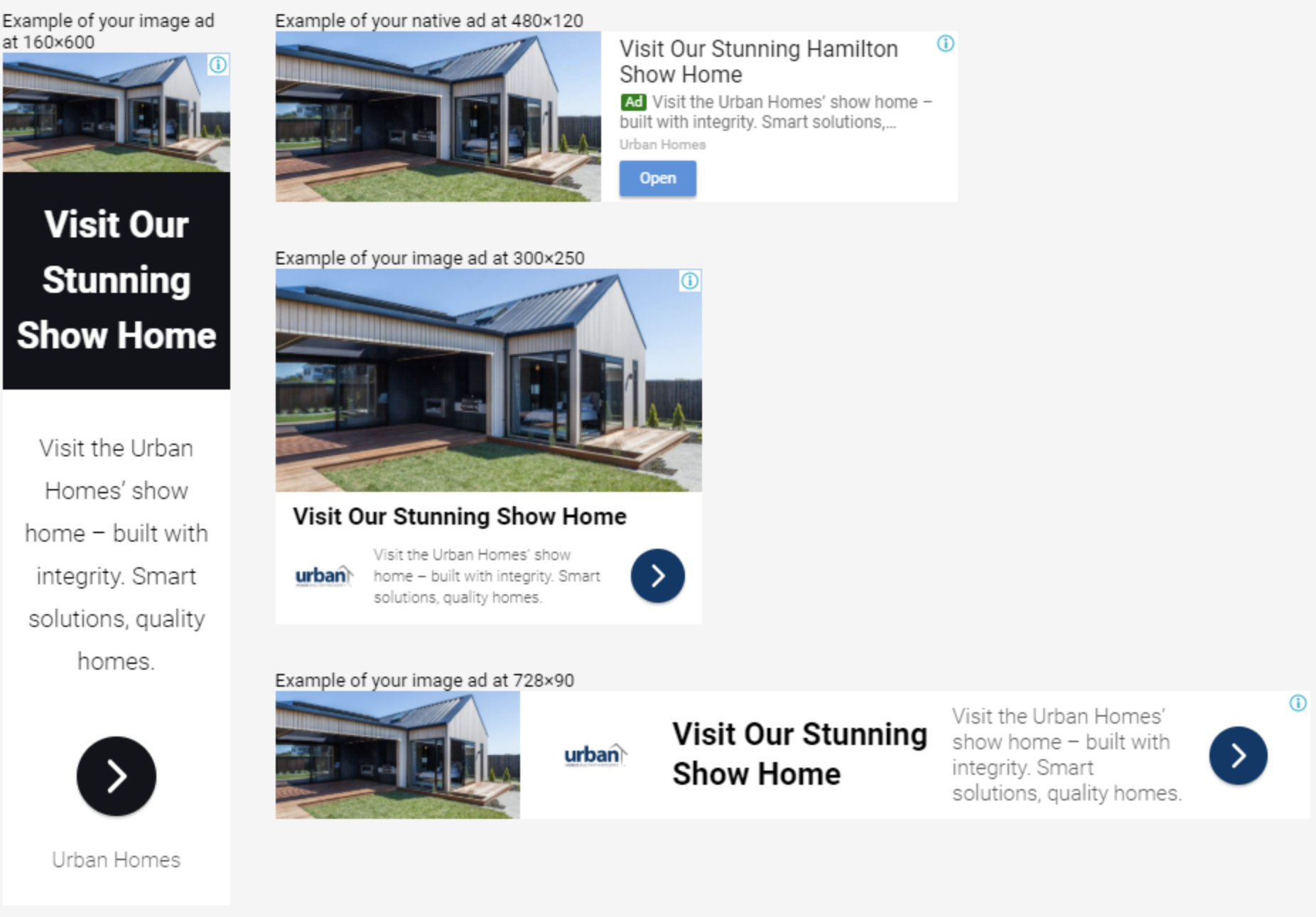
Key Benefits:
- Google will adjust the display of the ads to match the pages the ads are placed on (demonstrated in the image above)
- Your ads will be visible on external content that is relevant per your setting
- Effective in building awareness or remarketing
3. Video Ads
You can create compelling video campaigns with a range of video ad formats to engage customers in different ways on Google’s video partner sites, for example – YouTube! YouTube is a great platform to place your advertisements, thanks to its comparatively high conversion rate and the flexibility it provides.
There are numerous different types of Video Ads. Your ads can appear on the YouTube homepage, on search results pages, within the ‘related videos’ sidebar alongside videos, and within videos (at the start, middle, and/or end; either skippable or non-skippable), etc.
Learn more about the available video ad formats here:
- Skippable in-stream ads
- Non-skippable in-stream ads
- In-feed video ads
- Bumper ads
- Outstream ads
- Masthead ads
4. Shopping Campaigns
A shopping campaign allows you to add your promoted product to the product listings in Google’s Shopping tab.
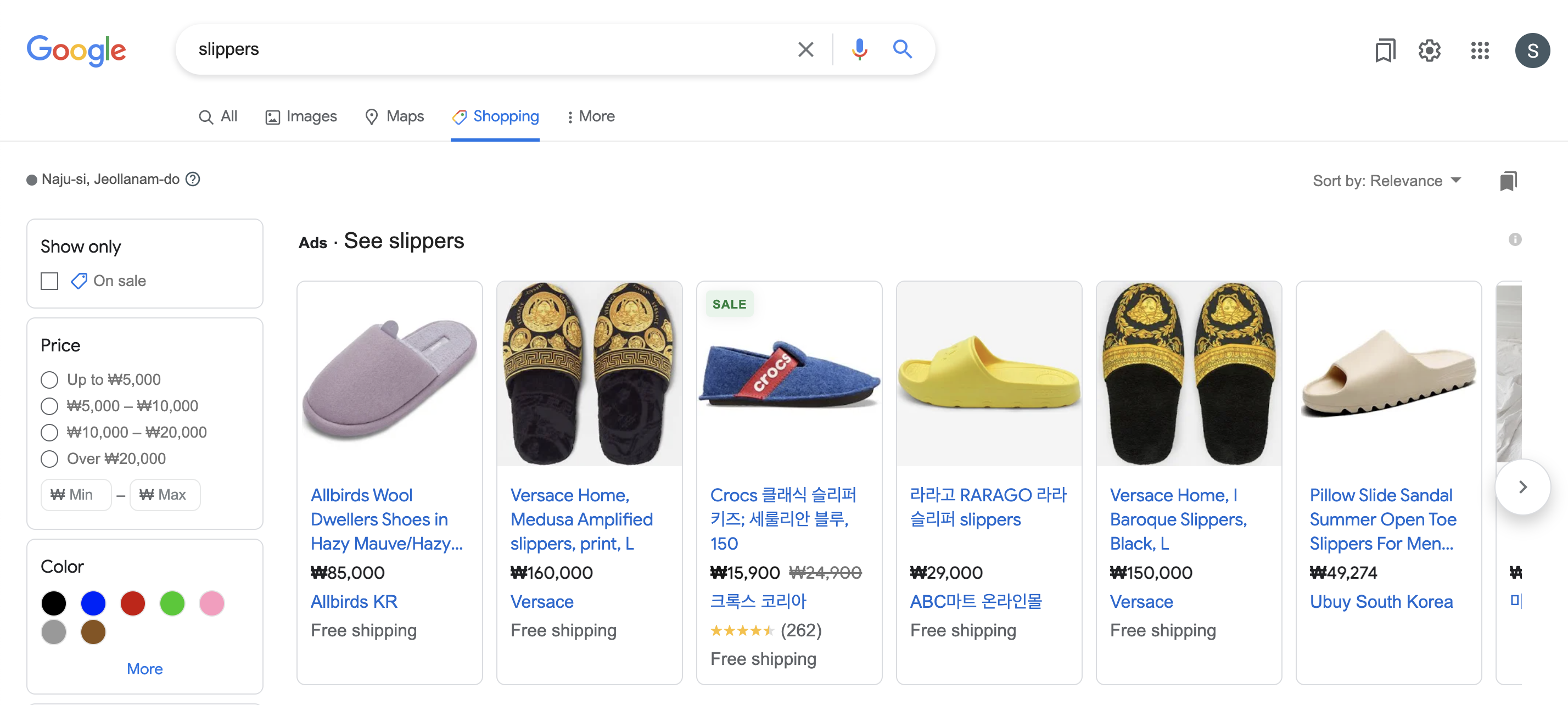
As shown in the image above, your product will come up in the ‘shopping’ tab/tag. This is a great way to boost your sales because people searching for the keywords are likely your potential buyers. Google lets you optimise the audience reach by the user’s demographic and geographical properties.
Note that you will first need to register to Google Merchant Centre where you can upload your product inventory to our account.
5. App Campaigns
If the purpose of your advertisement is to find new app users and increase the sales within your app, this campaign must be one of your considerations!
This type is almost fully automated (Google does most of the jobs for you) and comprehends a wide range of platforms. Your app will be promoted throughout Google’s largest properties encompassing Search, GooglePlay, YouTube, Discover on Google Search, and expansive Google Display Network.
Unlike most Google Ads campaigns, you don’t design individual ads for App campaigns. Instead, Google uses your ad text ideas, images, videos, and assets from your app’s store listing to design a variety of ads across several formats and networks.
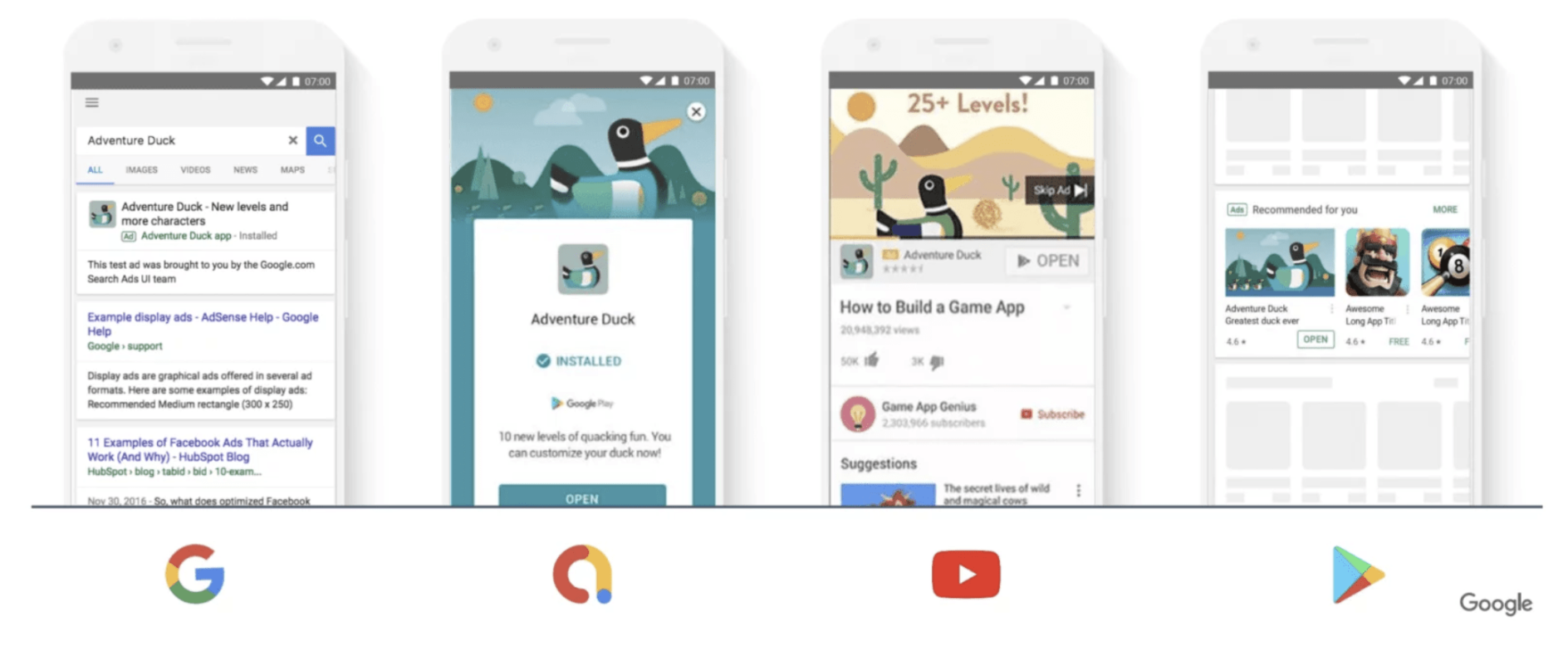
To get started, all you need to do is provide some text, a starting bid and budget, and let Google know the languages and locations for your ads.
Google systems will test different asset combinations and serve ads that are performing the best more often, with no extra work needed from you.
6. Local Campaigns
There is a common misconception that online advertisement is less effective in promoting offline stores. However, if you look back, it isn’t hard to recall the last time you searched for a physical store near you on Google.
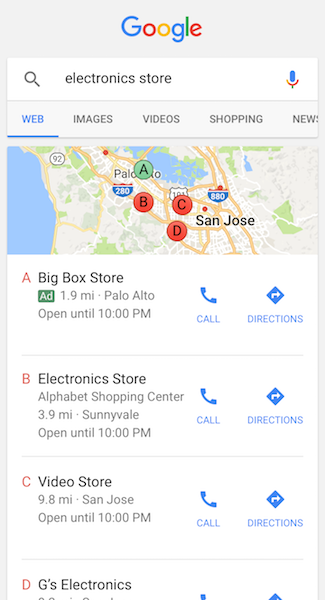
Many local keywords are packed with high action intent which leads to immediate conversion, and you can definitely take advantage of the local campaigns in Google Ads! Your ads will be automatically optimised to appear across Search, Display, Google Maps, and YouTube.
7. Smart Ads Campaign
Smart campaigns by Google includes all of the above options with automatic optimisation of channels and targeting done by Google! It is specifically more important and useful for small business owners due to lack of relevant resources and knowledge in online advertisement.
For small businesses with limited budget, it is important not to fail on its advertisement/campaigns resulting in lots of time spent to learn about online marketing or managing their ads. If this is your business’ concern, Smart Campaign is the right type for you since Google Ads will do most of the jobs for you!
Procedures are following:
- Set your business goals
- Input your budget and specify your location
- You are set to go! Google Ads detect search phrases that are relevant to your business and shows your ads to potential customers who are searching for what you offer. The performance is monitored constantly, and the Google’s algorithms are always learning how to better predict which user interactions will help you achieve your business goals
Example (from Google Ads official guideline)
The staff of a fish and chip shop in Derby, for example, may be too busy serving food during their shifts to dedicate any time to optimising the search phrases bids on each of their Google Ads. With Smart campaigns, they no longer need to manage this process manually. Google’s technology will identify terms like “haddock” and “battered sausage” as relevant to the business and automatically show ads to nearby potential customers searching for those terms.
Budgeting
One of the major advantages of using Google Ads is the fairness and flexibility in your advertisement budgets! Google Ads is PPC (pay-per-click) advertisement which means you pay a predefined amount of money for each click your advertisement gets. This puts you in control of the amount you want to spend, as well as where and how you spend it.
You start by bidding on keywords that people search on Google – related to your business for a chance to show ads in Google search results. Then you pay whatever you bid if, and only if, they click your ad to visit your website or call you.
Set your goals and budget
A thorough understanding of what you want to achieve through the ads is critical. It could be drawing more traffic to your website, getting more calls, building awareness of your business in particular locations, or among a certain customer demographic.
Assuming that your campaigns or advertisement are designed appropriately, you can set a maximum monthly ad budget. Google Ads will automatically adjust to optimise results towards achieving your goal(s) and stop showing your ads when you hit the predefined goal or spend all predefined budget.
You can set ‘daily limits’ in ad spend as well, but you need to be very careful with this. Google analyses the daily search traffic and it will show your ads more frequently on days when more people are searching, and thus your daily ad spend can differ from day to day.
Tips for Successful Operation of Google Ads
Here are a few tips to help you make the most out of your Google Ads.
1. Get familiar with the Google Ads UI
[Overview Tab]
The ‘Overview’ tab is an Account Manager’s dream come true and sums up everything you need to know about your account in one screen. Google Ads offers multiple semi-customisable windows within this Overview page that give you a quick and easy glance at your campaigns. (*Click on the triangle to expand the toggles for more information!)
- Need to know where your top ad views are coming from? There’s a geographical touch map for that:
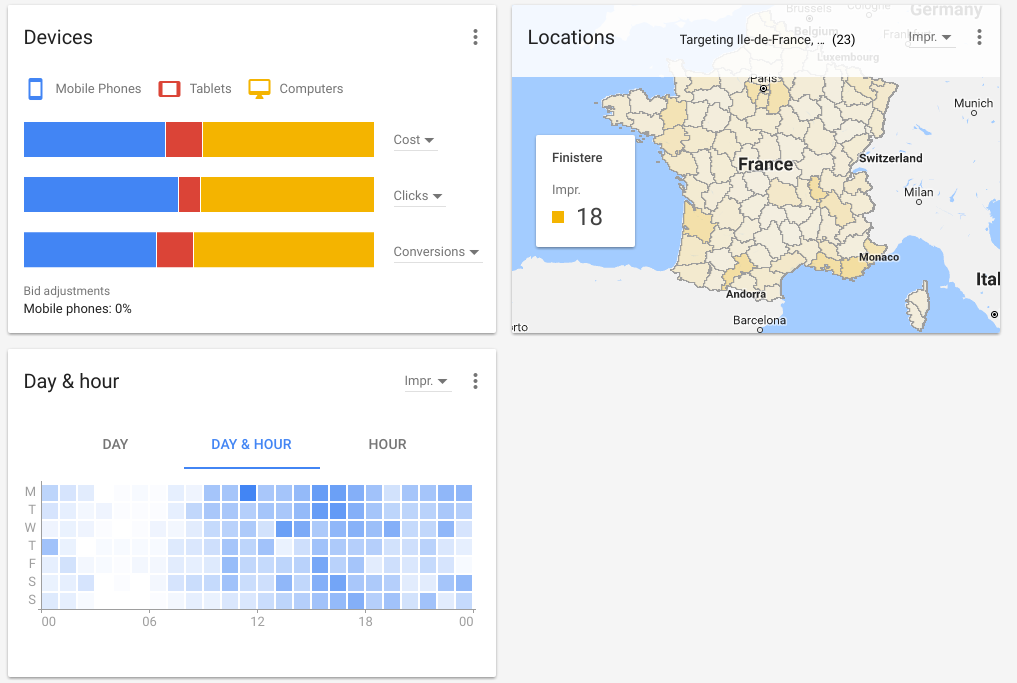
- Need to know what keywords are incurring how much cost? There’s a ranked and already sorted table for that:
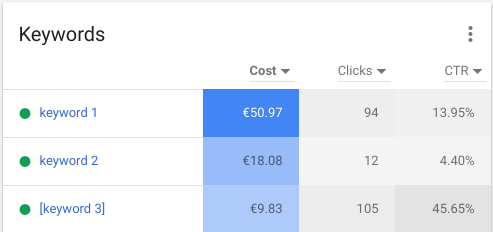
- Live Performance Graph & KPIs
- Your Overview Tab also gives you the live performance graph that the old AdWords interface used to offer. It includes a few KPIs at the top of the graph, which gives advertisers a nice quick summary of current performance.These KPIs include Clicks, Conversions, Cost/Conversion, and Total Cost. But you can get more in depth in the Reporting if you want.These graphs are great for WoW(week over week) or MoM(month over month) comparisons
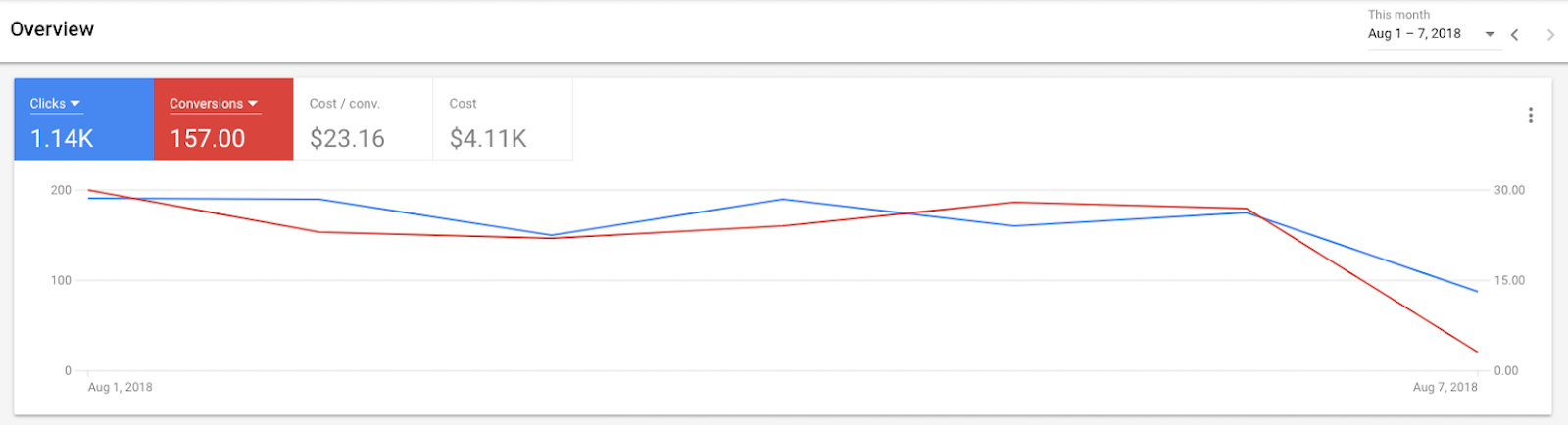
These graphs are great for WoW(week over week) or MoM(month over month) comparisons
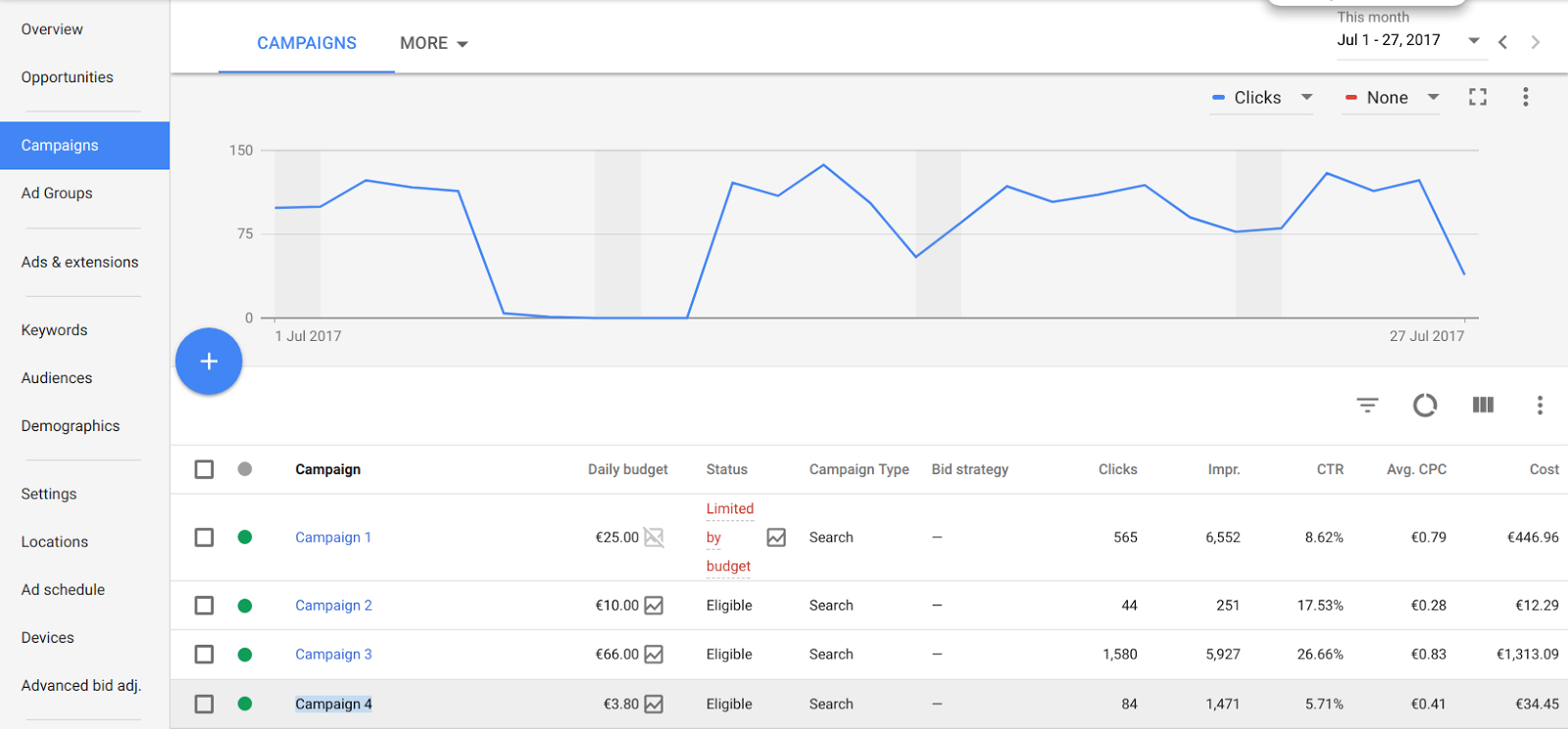
[Campaigns and Keywords]
You can go about your everyday tasks by accessing the sidebar on the left and head to “Campaigns”, “ad Groups”, or “Ads & Extensions” area. Then it’s fairly straight forward from there.

Keywords matching options are following:
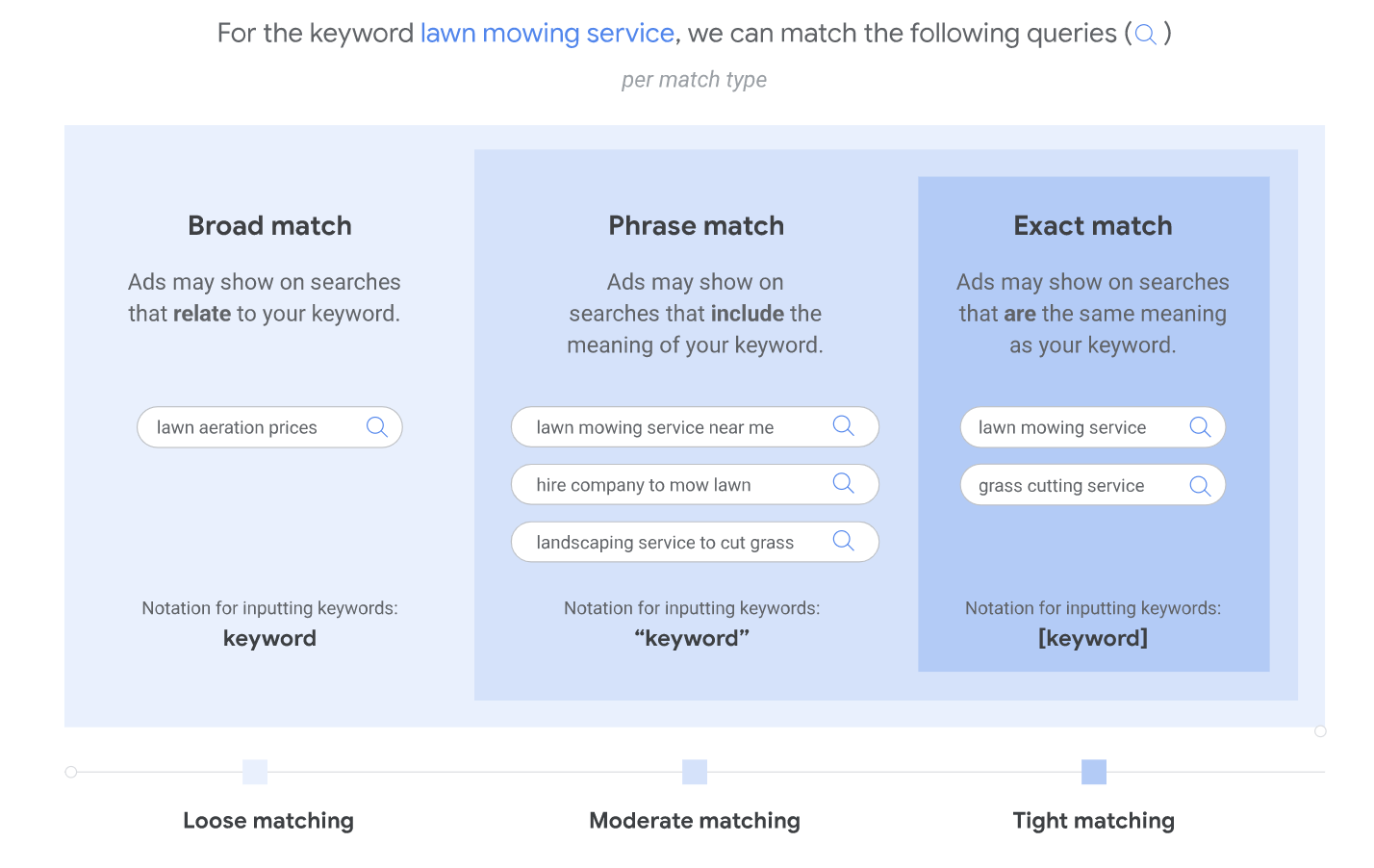
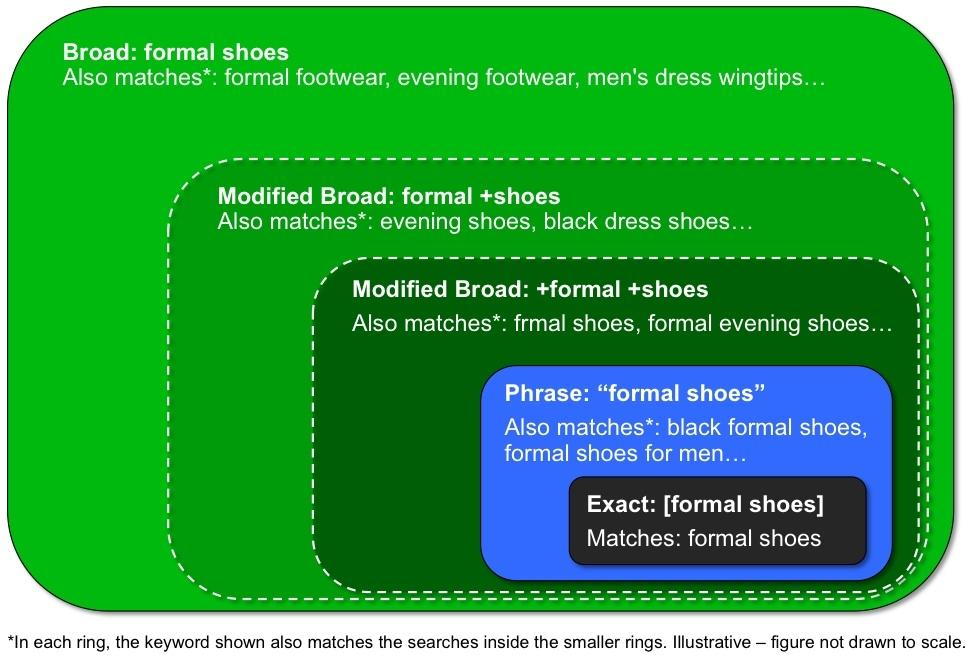
1) Broad Match:
Ads may show on searches that are related to your keyword, which can include searches that don’t contain the keyword terms. This helps you attract more visitors to your website, spend less time building keyword lists, and focus your spending on keywords that work. Broad match is the default match type that all your keywords are assigned, so that you don’t have to specify another match type (exact match, phrase match, or a negative match type).
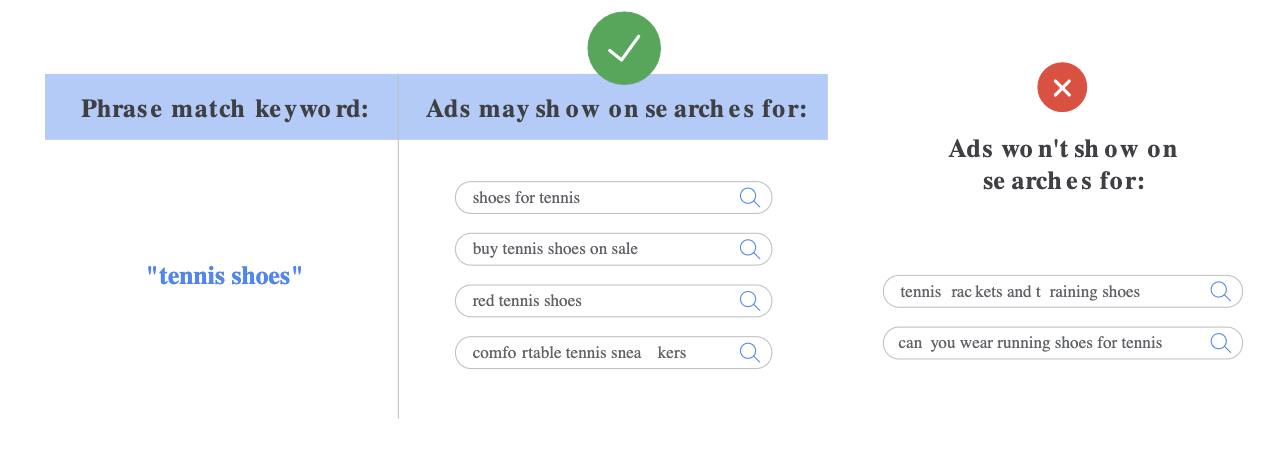
2) Phrase Match:
Ads may show on searches that include the meaning of your keyword. The meaning of the keyword can be implied, and user searches can be a more specific form of the meaning. With phrase match, you can reach more searches than with exact match and fewer searches than with broad match, only showing your ads on the searches that include your product or service.
The syntax for phrase match is to put quotes around your keyword, such as “tennis shoes”. Below is an example of how phrase match will work:
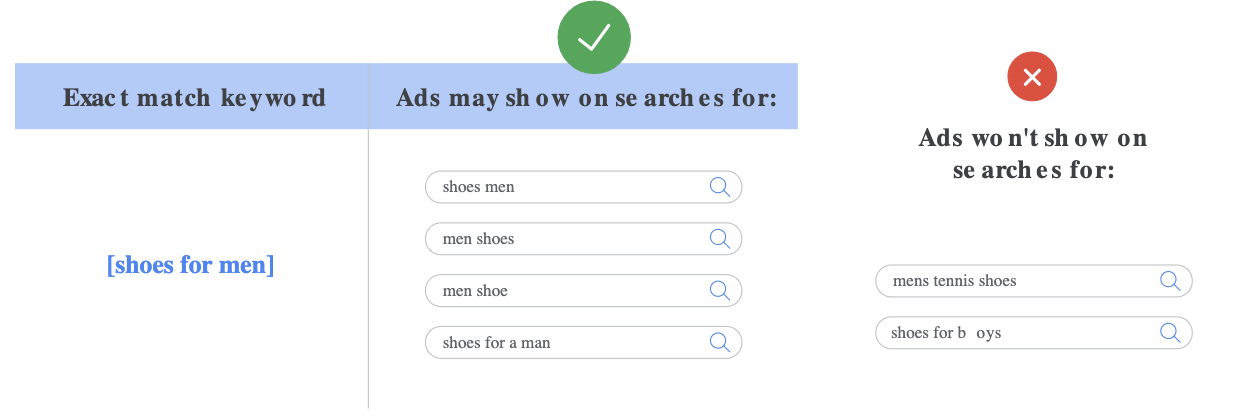
3) Exact Match:
Ads may show on searches that have the same meaning or same intent as the keyword. Of the 3 keyword matching options, exact match gives you the most control over who sees your ad, but reaches fewer searches than both phrase and broad match.
The syntax for exact match is to use square brackets, such as [red shoe]. Below is an example of how exact match will work:
[Navigation Menu]
The Navigation Menu is on the left hand side of the screen in dark grey. This shows your different campaign view options.
Depending on which view you click, you’ll see all of those campaigns populate on your main screen and under the four major tabs in your Navigation Menu.
[Page Menu]
This is where you can view all of the different strata (fancy people talk for “levels”) of your campaigns. For example, you can click-through to your distinct Ad Groups, Ads, Ad Extensions, Audiences, etc.
You can essentially view everything you need to within each campaign. More importantly, you can see all of the campaigns you could possibly be comparing to one another just to the left of this Page Menu (in the Navigation Menu).
[Subpage Menu]
The Subpage Menu will actually change depending on what you click in the Page Menu.
For example, clicking Ad Groups will give you the Subpage Menu showing Ad Groups and Auction Insights.
But, if you were to click through to the Ads & Extensions tab, you’d be shown a Subpage Menu like the image below:
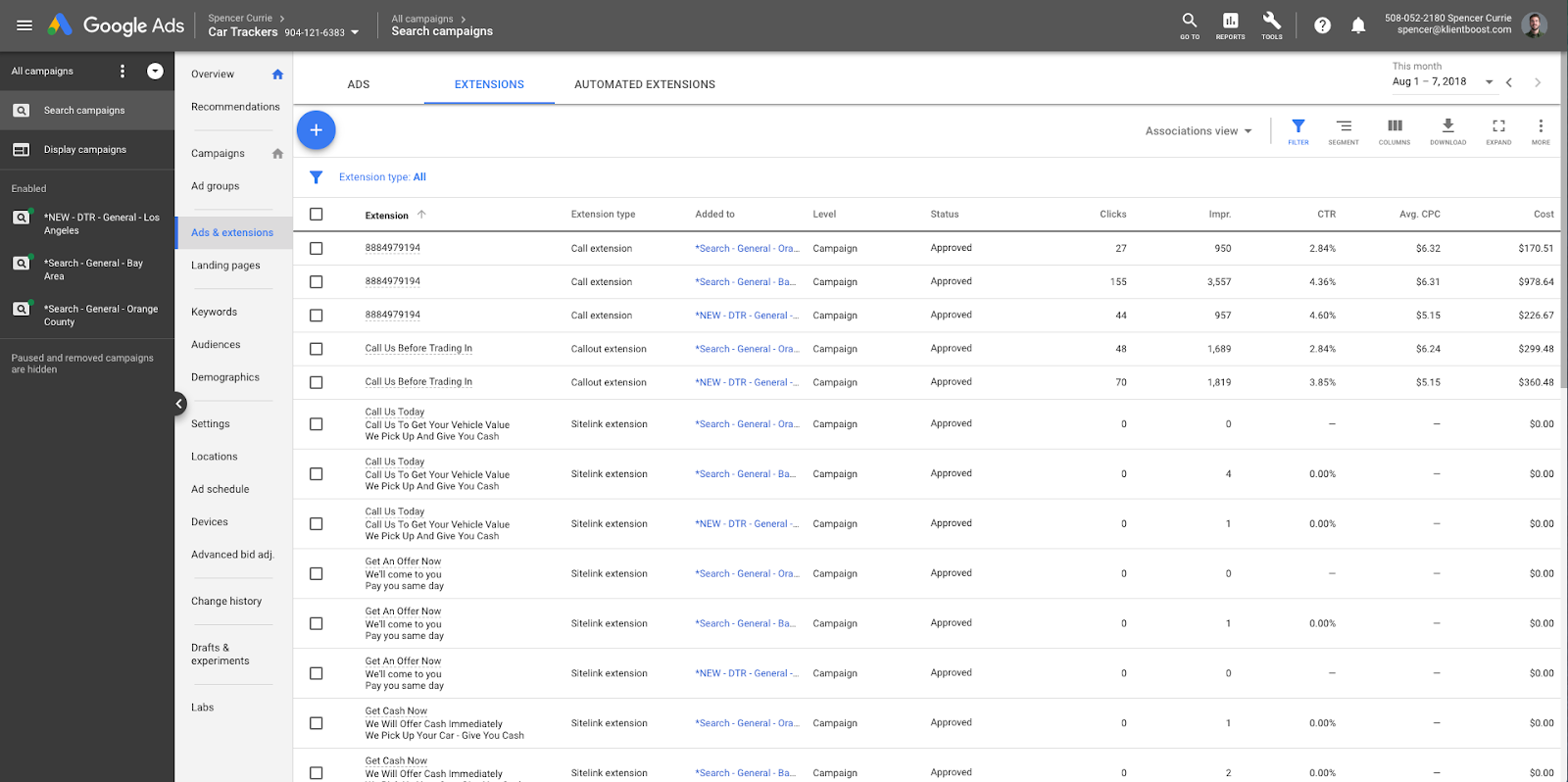
Depending on what you click, the necessary options for that tab will be shown in the Subpage menu.
[Top Bar]
The Top Bar is the consistent toolbar that will help you navigate through your actual Google Ads account. Note that this is where the search bar is!
[Tools Tab]
To find your actual Tools and different PPC functions, you have to find the Toolbar at the top of the page.
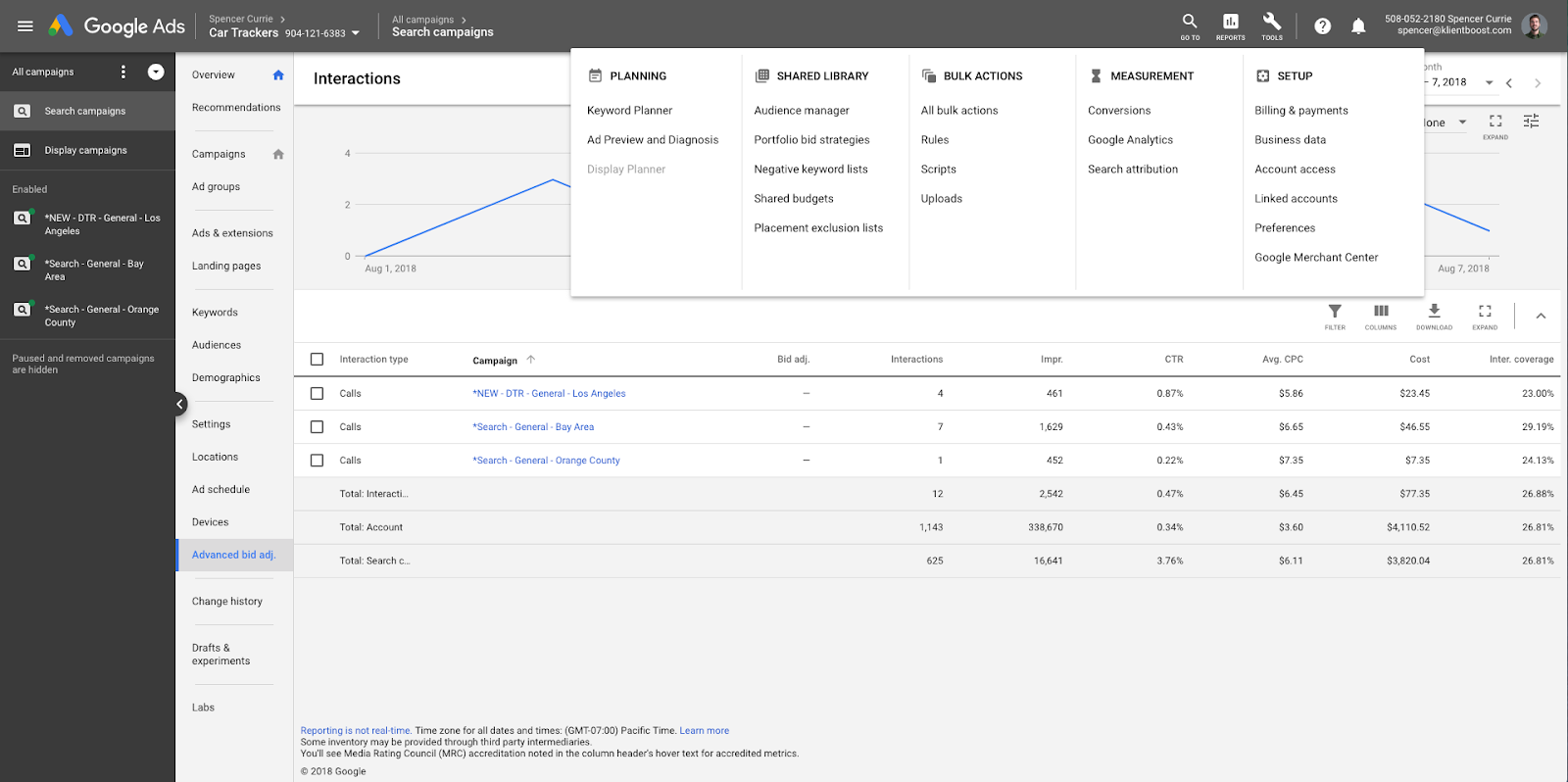
The Tool Tab can be found on the Top Bar of Google Ads. It has a tool wrench as an icon. When you click it, a drop down menu will appear that shows you the different options and actions available out of five categories:
- Planning
- Shared Library
- Bulk Actions
- Measurement
- Setup
Within the Planning category you’ll be able to access your Keyword Planner and preview your Ads. You can also view your Display Planner, if you’re running display campaigns.
[Shared Library]
In the Shared Library, you’ll be able to manage all of your vital targeting information, including:
- Budgets
- Bid Strategies
- Audiences
- Negative Keyword Lists
- Placement Exclusion Lists
These are highly valuable assets in PPC; building out these lists will help eliminate wasteful spend and improve ROAS.
The Bulk Action section still handles all of your bulk actions for campaigns, ad groups, etc. (i.e. Rules, Scripts, Uploads).
Lastly, your Tools Tab includes the Measurement section where you can view your Conversions and choose Attribution Models. You can also click through to Google Analytics if you need more data.
Setup features, including Billing, Account access, and your Google Merchant Center are all under the Setup Tab.
[Search Feature]
The next Go To function in the Top Bar, right next to the Reports and Tools buttons, lets you go straight to any page in Google Ads.
Keep in mind, however, that this search feature doesn’t let you go to specific campaigns. You can view pages from within the Page Menu, nothing more. So it’s more of a navigational tool than a discovery tool.
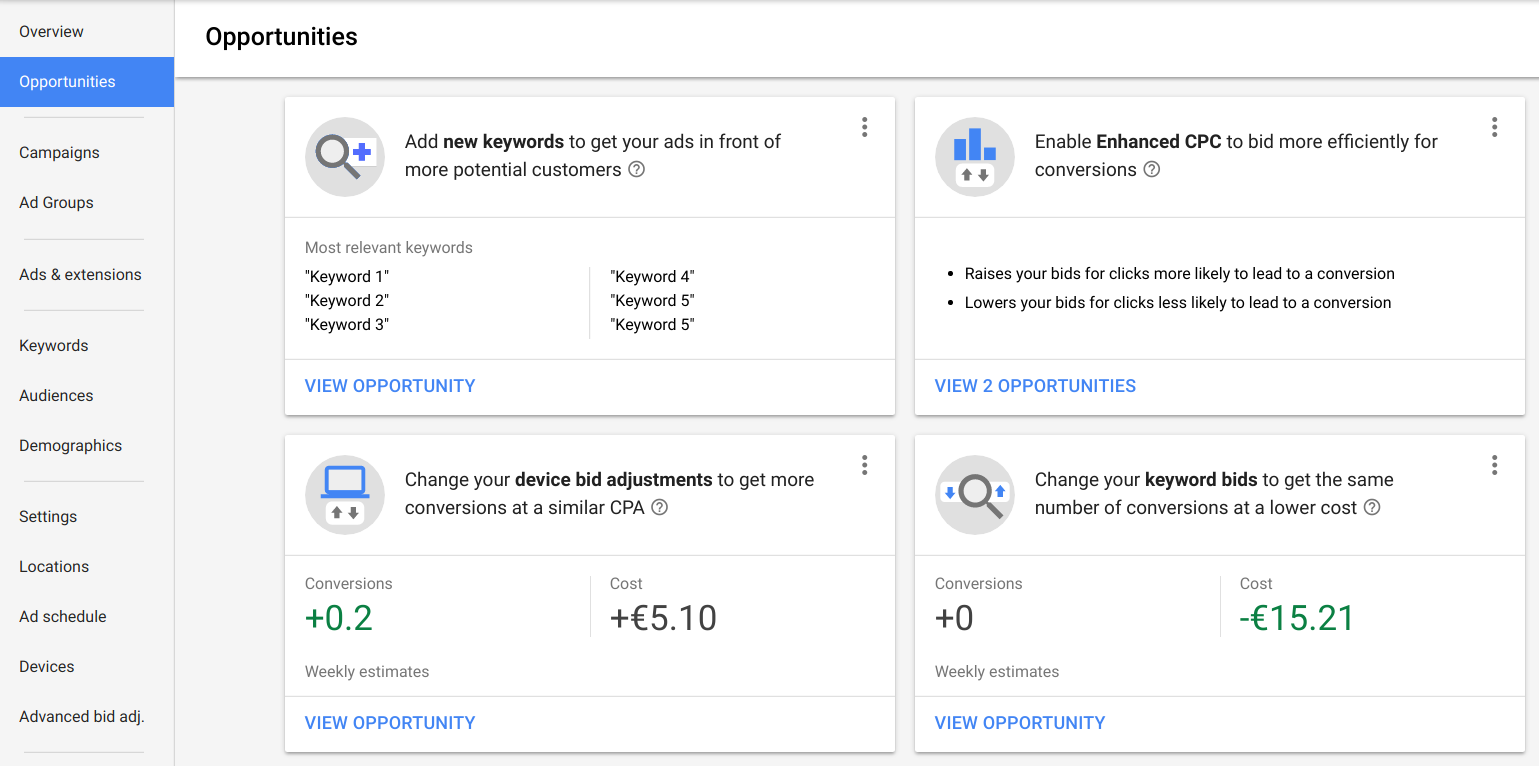
[Opportunities]
You can access this dashboard by heading to “Opportunities” and then everything is split into a ‘before vs after’ style. Not only does it provide a sense of direction, but it’s really indicative of account health and makes it easy to improve overall efficiencies.
[Reports]
Simply head to the view you wish to export, and you’ll find this feature under the options dropdown:
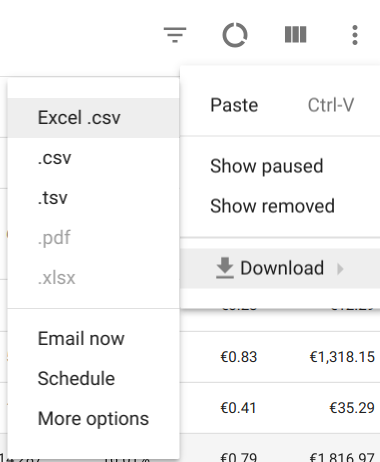
If you need Google Sheets Integration, Google Ads has a Google Sheets Plugin, making these reports that much easier.
2. Structure your Account
When someone searches on Google.com and scans the results, your ad can stand out more if it’s more relevant to what they were looking for. To do this, you select keywords that you’d like to show an ad for and cluster them into themed ad groups so that you can show ads related to those keywords. You can also separate your ad groups into campaigns to allocate your budget to the topics that are most important to you.
For example, let’s say your organisation gives free books to children. You probably don’t want to run only one campaign about ‘Books’. Instead, your campaigns might look like following:
- Campaign: Books for Babies
- Campaign: Books for Preschoolers
- Campaign: Books for Teens
- Campaign: Volunteer
- Campaign: Donate
Then, your ad groups would reflect how a person might search on Google.com so you can offer ads that are very relevant to their search.
For example, ad groups within a campaign called ‘Volunteer’ might include:
- Volunteer with babies
- Volunteer with children
- Volunteer in education
- Volunteer for literacy
- Volunteer to teach children to read
3. Create effective advertisements
Write at least 3 compelling ads per ad group that are relevant to the keywords in that ad group. The ads will rotate and prioritise the ads that are performing better than others in the ad group.
For example: if you create 2 Expanded Text Ads and 1 Responsive Search Ad, which will allow you to key in 15 headlines and 4 descriptions, while Google will help you to combine the ads by choosing 3 headlines and 2 descriptions based on users’ search terms. You may get more info here: https://support.google.com/google-ads/answer/7684791?hl=en
Short, non-repetitive sentences work best. Avoid uncommon acronyms and abbreviations. Identify the unique aspects of your organisation and service, such as ‘Check our free book database to find books your preschooler will love’ or ‘Volunteer to read to children in your community today’.
Sample ad copy #1:
- Teach children how to read
- Volunteers needed now
- Online training available
- www.TeachKidsToReadNow.org
Ad extensions add useful links below the ad that help your message get noticed. Learn about the various ad extensions and how to use them.
Structured Snippets: https://support.google.com/google-ads/answer/6280012
4. Choose the right keywords
Ask yourself which keywords – word combinations and phrases – you would type into the Google search box to find your organisation’s programmes and services. Then, use the Keyword Planner to find related keywords and group them together in ad groups if you’d want to show the same ad for them.
If you add a keyword without any formatting, the AdWords programme keyword default is broad match. For example, if your keyword were breast cancer, your ad would show when a Google search includes the keyword breast cancer, regardless of other search terms used or the order in which a user typed them.
Your ads will also automatically show for expanded matches, including plurals and relevant variations such as:
- breast cancer information
- cancer of the breast in men
- support groups breast cancer
- breast cancer symptoms
- self breast exam to detect cancer
All of the queries above are related to breast cancer and are relevant. However, the broad match default doesn’t work well for general keywords that may be included in searches unrelated to your organisation.
Let’s say your organisation is devoted to saving endangered bears. Here are search queries that might display an ad targeted to the broad match keyword bears:
- chicago bears
- berenstain bears video
- collectible teddy bears
- bad news bears dvd
None of the searches listed above are relevant to the organisation, yet they all include the keyword bear. Keywords such as protect bears and endangered bears would be a better option. In these cases, you could use negative keywords. You can specify keywords as negatives by preceding an unwanted keyword with a hyphen.
For example, if our endangered bear organisation wanted to use the keyword bear, the following negative keywords should be listed to avoid showing on unrelated queries:
- -chicago
- -berenstain
- -bad news
- -teddy
5. Target the right audience
You can also target your ads to different geographic locations and languages. Options include setting a specified distance from your organisation’s service area to selecting cities, regions or nations.
6. Track actions people take after clicking on your ads
In addition to Google Ads showing how many people clicked on your ads, Google Ads or Google Analytics can track what customers do once they’ve arrived at your site.
For example, let’s say some of your keywords lead to people browsing your website while others lead to people signing up for your newsletter or making a donation. Knowing this would help you determine what types of keywords and ads to set up for future fundraising campaigns.
Ask your webmaster to install the AdWords conversion tracking code on your website or consult your donation payment provider to embed your tracking code in their system. Or you can import goals from Google Analytics to track in AdWords. Just make sure to use the same email address for both your AdWords and Analytics accounts so that they can be easily linked together. Learn more about linking your accounts.
Adding a conversion tracker can also allow you to better manually target CPA (cost per acquisition) or ROAS (return on ad spending). These are more advanced metrics that perform better when they are driven by in-depth conversion data which is why a conversion tracker is necessary.
You can also directly link your Google Analytics Account and Google Ads Account, and you can set up goals in Google Analytics then import the tracking data to Google Ads, in order to further evaluate on Google Ads performance. You may refer to: https://support.google.com/google-ads/answer/1704341?hl=en&co=ADWORDS.IsAWNCustomer
7. Automatically set bids
Automating your bids with Google Ads can save you time optimising for your goals. Maximise conversions, which is a Smart Bidding strategy, automatically sets bids to help get the most conversions for your campaign while spending your budget. Maximise conversions bidding strategy will identify which keywords are more likely to result in a desired action and will then bid more for those and less for others. You can turn on Maximise conversions on the Settings tab of your campaigns. Note that the bidding strategies can differ depending on your objectives.
Note: In Ad Grants, using Maximise conversions allows the system to bid over the programme-level $2.00 USD max bid if your account’s performance merits doing so.
Setting up Conversion Tracking:
A brief video explaining how to enable conversion tracking with Google Tag.
References
- Video that explains Google Ads Bidding Strategies! The strategies are already provided by Google Ads, you just need to learn and choose the ones that suit your objectives!
PS!
At FSI we’re always seeking to improve, so if you have any feedback on this guide/template, please do not hesitate to let us know.



